Masimo Secures FDA Clearance for Expanded Use of O3® Regional Oximetry Delta Hemoglobin Parameters Across All Patient Populations
Masimo has announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted 510(k) clearance for the expanded use of its O3® Regional Oximetry delta hemoglobin parameters, an advancement that broadens the clinical utility of the technology across a wide range of applications and patient populations, including pediatrics and neonates. This regulatory milestone allows healthcare providers to integrate delta hemoglobin insights into both cerebral and somatic monitoring, strengthening Masimo’s position as a leader in advanced patient monitoring technologies.
Expanding the Role of O3® Regional Oximetry
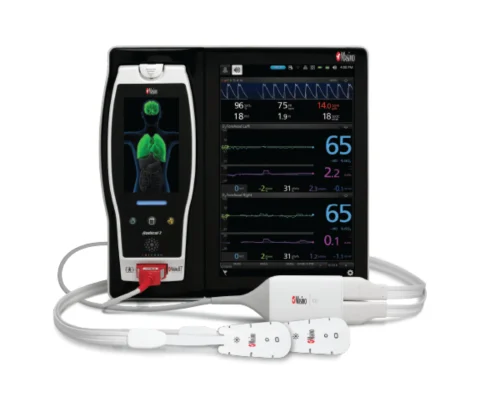
O3® Regional Oximetry, available on the company’s Root® Patient Monitoring and Connectivity Platform, utilizes near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) to measure and display continuous regional oxygen saturation (rSO2) values in targeted tissues. These values reflect the dynamic balance between oxygen delivery and the metabolic needs of organs or tissues.
Traditionally, rSO2 readings have been valuable in identifying whether tissues are receiving adequate oxygen. However, standalone rSO2 data often cannot reveal the underlying cause of an imbalance. For instance, a low saturation value may result from a drop in blood oxygen content, reduced blood flow, or increased tissue oxygen consumption. Without additional information, clinicians may face uncertainty in determining the appropriate intervention.
The FDA clearance of delta hemoglobin parameters (ΔcHb, ΔHHb, and ΔO2Hb) directly addresses this challenge. These values represent relative changes in:
- Total hemoglobin (cHb) – indicating overall hemoglobin presence in tissue.
- Deoxygenated hemoglobin (HHb) – reflecting venous blood and oxygen consumption.
- Oxygenated hemoglobin (O2Hb) – indicating arterial oxygen delivery.
By providing real-time tracking of these changes, clinicians can better identify the physiological mechanisms driving fluctuations in rSO2 and tailor patient care with greater precision.
Clinical Relevance of Delta Hemoglobin Parameters
The addition of delta hemoglobin metrics offers actionable insights that help clinicians distinguish between conditions that may present with similar rSO2 readings. For example:
- Venous Congestion – An increase in total hemoglobin (ΔcHb) can indicate pooling of blood in tissue, which has been linked to negative outcomes such as flap failure in reconstructive surgery.
- Reduced Oxygen Delivery – Declines in oxygenated hemoglobin (ΔO2Hb) may point toward impaired arterial blood flow or lower oxygen content in circulating blood.
- Increased Oxygen Extraction – Rising deoxygenated hemoglobin (ΔHHb) may suggest elevated tissue oxygen demand or metabolic stress.
This layered view allows clinicians to differentiate between whether a patient’s tissues are under stress due to delivery deficits, venous congestion, or rising metabolic demand—each of which requires a distinct clinical response.
Evidence Supporting Broader Use
Masimo’s expanded clearance is underpinned by a growing body of evidence that supports the clinical value of incorporating delta hemoglobin monitoring into practice.
Randomized Controlled Trial in Elderly Surgical Patients
A 2024 randomized controlled trial in Korea evaluated the role of delta hemoglobin parameters in maintaining cerebral physiology during surgery under general anesthesia. Researchers compared outcomes between patients monitored with traditional oximetry (rSO2 alone) and those receiving comprehensive monitoring, including ΔcHb, ΔHHb, and ΔO2Hb.
Findings demonstrated that the expanded monitoring provided superior insights into changes in cerebral blood flow and cerebral metabolic rate, ultimately improving the ability to manage oxygen delivery and demand. The authors concluded that adopting delta hemoglobin monitoring “may be crucial for ensuring optimal management of cerebral physiology” in elderly surgical patients, potentially enhancing both safety and clinical outcomes in this vulnerable population.
Publications in Cardiac Surgery
Earlier studies also highlight the parameters’ clinical importance. A 2022 article in Anesthesia & Analgesia examined the challenges of traditional cerebral oximeters, which cannot reveal the exact etiology of desaturation events. Anesthesiologists often must rely on additional modalities to determine whether desaturation arises from blood flow changes, oxygen content variations, or venous congestion.
By integrating Masimo’s delta hemoglobin parameters, clinicians were able to characterize desaturation events more accurately. The study emphasized that variations in ΔHHb, ΔO2Hb, and ΔcHb provide critical information about changes in cerebral metabolism, arterial cerebral blood flow, and venous congestion—all of which influence patient management strategies during cardiac surgery.
A Complementary Role Alongside SedLine® Brain Function Monitoring
One of Masimo’s strategic advantages lies in integrating O3 Regional Oximetry with SedLine® Brain Function Monitoring, both of which operate on the Root® platform. Together, they create what the company calls a “Brain Health Platform”—the only available multimodal solution offering comprehensive, bilateral brain data on a single monitoring system.
- SedLine provides insight into brain electrical activity, reflecting oxygen demand.
- O3 with delta hemoglobin parameters provides detailed information about oxygen delivery and tissue saturation balance.
This combined view enables clinicians to evaluate both supply and demand dynamics within the brain, helping guide timely and informed interventions in anesthesia and critical care settings.
Dr. Basil Matta, Masimo’s Senior Vice President of Global Clinical Affairs & Solutions, highlighted the impact of this integration:
Ensuring vital organs and tissues are receiving enough oxygen to meet their metabolic needs is the cornerstone of optimal anesthesia and critical care. By using SedLine and O3 together, clinicians can investigate why the balance between delivery and demand has shifted—taking advantage of complementary information to restore physiological equilibrium.
Precision and Reliability
O3 Regional Oximetry is designed to provide both trending and absolute accuracy, giving clinicians confidence in the reliability of its data. According to Masimo, O3 demonstrates:
- 3% ARMS trending accuracy across cerebral and somatic monitoring for all ages.
- 4% ARMS absolute accuracy for adult cerebral monitoring.
- 5% ARMS absolute accuracy for pediatric cerebral and adult non-cerebral monitoring.
These performance benchmarks ensure that the technology delivers clinically relevant, trustworthy data—an essential feature when monitoring fragile populations like neonates or critically ill patients.
Transforming Clinical Assessment
The clearance for expanded use of delta hemoglobin parameters significantly enhances the value of O3 monitoring by:
- Broadening Patient Access – Now available for all patient groups, including the most vulnerable pediatric and neonatal populations.
- Expanding Clinical Applications – Effective in both cerebral and somatic monitoring, supporting use across diverse clinical scenarios.
- Driving Better Decisions – Enabling clinicians to pinpoint whether changes in rSO2 stem from delivery, congestion, or metabolic demand.
- Supporting Personalized Care – Providing individualized physiological insights that align with modern precision medicine approaches.
Masimo’s Continued Innovation in Patient Monitoring
The FDA’s clearance marks another milestone in Masimo’s broader mission to revolutionize noninvasive monitoring. With O3 and SedLine integrated on the Root platform, clinicians gain a powerful set of tools for evaluating cerebral and systemic oxygenation. The expanded capabilities underscore Masimo’s commitment to delivering comprehensive, multimodal solutions that adapt to the complexity of patient physiology.
By enhancing the ability to interpret changes in oxygenation with greater specificity, delta hemoglobin parameters may help prevent complications, improve patient outcomes, and support more efficient use of healthcare resources.