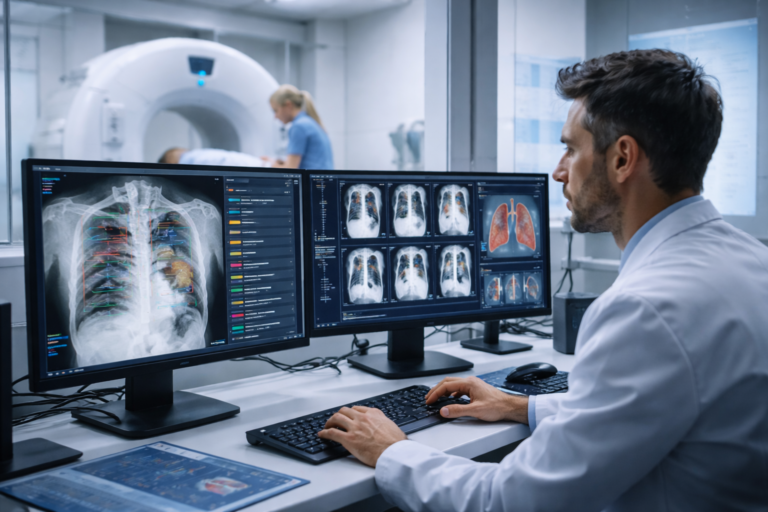
CureMetrix® has announced a new peer-reviewed study confirming the effectiveness of its investigational AI-enabled software for automated breast arterial calcification (BAC) detection in mammograms. This technology can inform personalized risk predictions for mortality and cardiovascular disease in women. The study showed that BAC reporting was both feasible and reliable when using the AI algorithm within the validated proprietary software cmAngio®*.
A recent study titled “Automated Breast Arterial Calcification Score is Associated with Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality,” published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) Advances on September 26, 2024, has validated the effectiveness of an AI algorithm for personalized detection and segmentation of breast arterial calcification (BAC).
The study analyzed the relationship between the presence and extent of BAC and cardiovascular disease (CVD) outcomes. It involved a retrospective review of over 18,000 women, tracking them for up to 11 years, and utilized an AI-generated BAC score assessed as both a binary and continuous variable.
Regression analyses evaluated the link between BAC and adverse outcomes, including acute myocardial infarction, heart failure, stroke, and mortality, while adjusting for factors such as age, race, diabetes, smoking, blood pressure, cholesterol, and history of CVD and chronic kidney disease.
Kevin Harris, president of CureMetrix, stated, “It’s exciting to have scientific validation of the feasibility and clinical relevance of using AI to accurately detect and score breast arterial calcifications on mammograms, potentially improving personalized CVD risk stratification.” He emphasized the importance of collaboration among cardiology, radiology, and primary care teams to enhance preventative healthcare for women.
The study revealed that each 10-point increase in an individual’s BAC score (Bradley Score™: 0-100) was linked to an 8% higher mortality risk (HR 1.08 [95% CI 1.06-1.11]) and an 8% increased risk of composite outcomes (HR 1.08 [95% CI 1.06-1.10]). Notably, BAC was particularly predictive among younger women aged 40-59, with patients showing three times the odds of adverse outcomes, including myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, and mortality (composite outcome OR = 3.18, 95% CI: 2.81 – 3.61), highlighting the potential for early intervention.
Conducted using anonymized patient records at UC San Diego Health, the research aims to raise awareness of breast arterial calcifications as a cardiac risk factor. Lori B. Daniels, MD, MAS, FACC, senior author and Professor of Cardiology at UC San Diego School of Medicine, expressed hope that these findings would leverage routine screenings for preventative cardiovascular care.
For detailed information, see the full paper at JACC. Some authors have consulted for CureMetrix, and others are employees. The first and senior authors had independent access to all data and drafted the manuscript.
*cmAngio® is FDA-cleared for BAC detection and localization but is not a diagnostic tool for specific diseases. The version that provides the Bradley Score is for research purposes only and is not commercially available.
About CureMetrix
CureMetrix is dedicated to advancing technology that enhances disease detection and improves survival rates globally. Collaborating with radiologists, cardiologists, and leading institutions, CureMetrix develops algorithms to impact women’s healthcare, addressing conditions from breast cancer to heart disease. The company aims to save lives through early and accurate detection, improving clinical and financial outcomes, and delivering reliable technology for doctors, healthcare systems, and patients.